Motion component
Most React animations in Motion are powered by the <motion /> component.
There's a motion component for every HTML and SVG element, for instance motion.div, motion.circle etc. It extends standard React components with animation props that run at up to 120fps - without triggering React re-renders.
Usage
Import motion from Motion:
// React import { motion } from "motion/react" // React Server Components (Next.js etc) import * as motion from "motion/react-client"
You can use a motion component exactly as you would any normal HTML/SVG component:
<motion.div className="box" />
But you also gain access to powerful animation APIs like the animate, layout, whileInView props.
<motion.div className="box" // Animate when this value changes: animate={{ scale: 2 }} // Fade in when the element enters the viewport: whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} // Animate the component when its layout changes: layout // Style now supports indepedent transforms: style={{ x: 100 }} />
Building with AI? The Motion Studio MCP gives your AI editor access to the latest docs and source code of 330+ examples.
Performance
motion components bypass React's render cycle entirely. Animated values update on every frame via the browser's native animation pipeline, so even complex animations with dozens of animated properties won't cause React re-renders or style/layout thrashing.
Using motion values instead of React state to update style will also avoid re-renders.
const x = useMotionValue(0) useEffect(() => { // Won't trigger a re-render! const timeout = setTimeout(() => x.set(100), 1000) return () => clearTimeout(timeout) }, []) return <motion.div style={{ x }} />
Check your MotionScore
Enter a URL to audit your site's animation performance.
Server-side rendering
motion components are fully compatible with server-side rendering, meaning the initial state of the component will be reflected in the server-generated output.
// Server will output `translateX(100px)` <motion.div initial={false} animate={{ x: 100 }} />
Custom components
You can add motion capabilities to any React component with motion.create(). The returned component accepts all standard motion props (animate, whileHover, drag, layout, etc.) alongside the original component's props.
const MotionComponent = motion.create(Component)
Your component must pass a ref to the component you want to animate.
React 18: Use forwardRef to wrap the component and pass ref to the element you want to animate:
const Component = React.forwardRef((props, ref) => { return <div ref={ref} /> })
React 19: React 19 can pass ref via props:
const Component = (props) => { return <div ref={props.ref} /> })
Make sure not to call motion.create() within a React render function! This will make a new component every render, breaking your animations.
It's also possible to pass strings to motion.create, which will create custom DOM elements.
// Will render <custom-element /> into HTML const MotionComponent = motion.create('custom-element')
By default, all motion props (like animate etc) are filtered out of the props forwarded to the provided component. By providing a forwardMotionProps config, the provided component will receive these props.
motion.create(Component, { forwardMotionProps: true })
Stay in the loop
Sign up for the Motion newsletter.
Props
motion components accept the following props.
Animation
Motion provides declarative animation props like animate and exit. Learn more about React animations in Motion.
initial
The initial visual state of the motion component.
This can be set as an animation target:
<motion.section initial={{ opacity: 0, x: 0 }} />
Variants:
<motion.li initial="visible" />
<motion.div initial={["visible", "active"]} />
Or set as false to disable the enter animation and initially render as the values found in animate.
<motion.div initial={false} animate={{ opacity: 0 }} />
animate
A target to animate to on enter, and on update.
Can be set as an animation target:
<motion.div initial={{ boxShadow: "0px 0px #000" }} animate={{ boxShadow: "10px 10px #000" }} />
Or variants:
<motion.li animate="visible" />
<motion.div initial="hidden" animate={["visible", "active"]} />
exit
A target to animate to when a component is removed from the tree. Can be set either as an animation target, or variant.
Owing to React limitations, the component being removed must be a direct child of AnimatePresence to enable this animation.
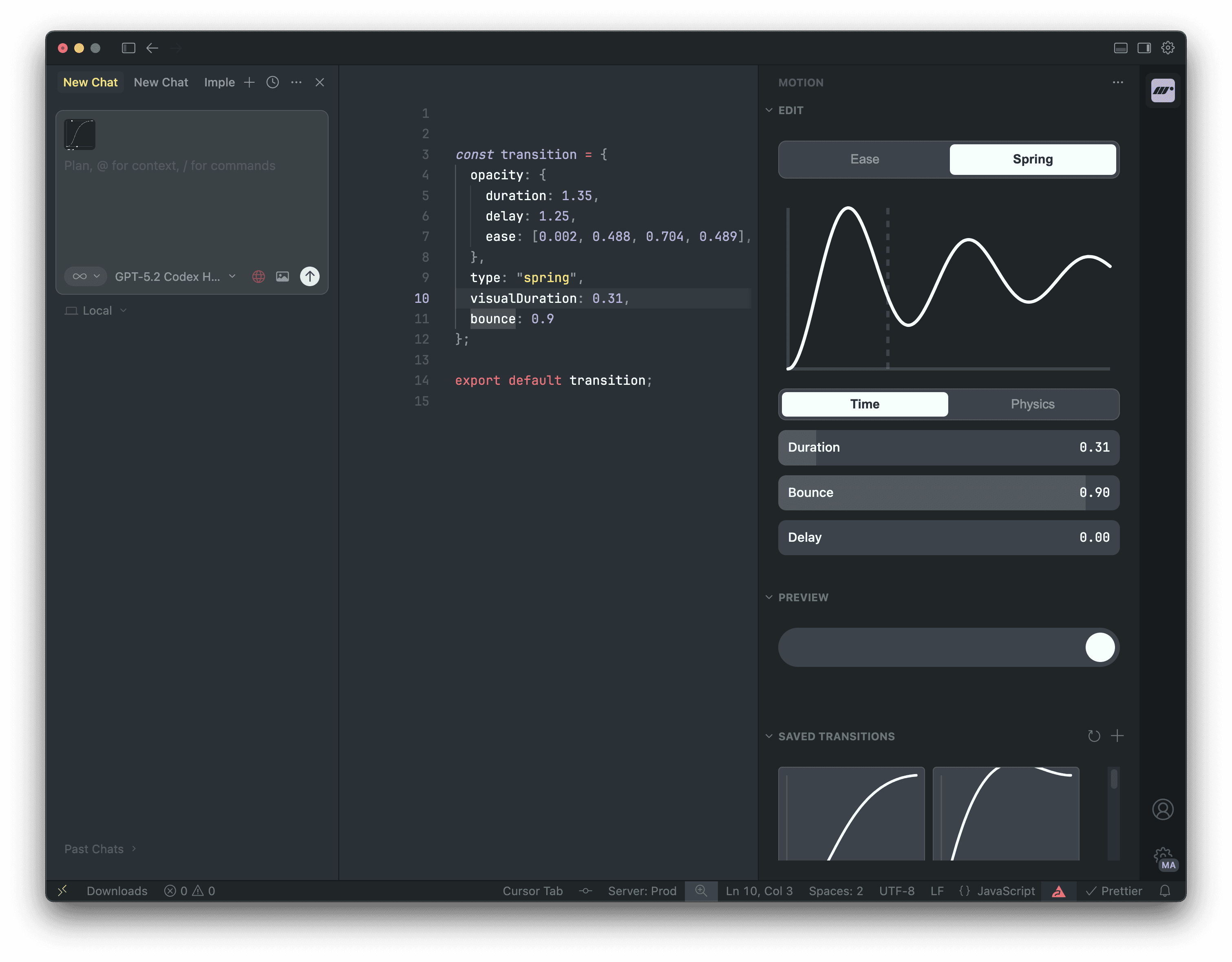
transition
The default transition for this component to use when an animation prop (animate, whileHover etc) has no transition defined.
<motion.div transition={{ type: "spring" }} animate={{ scale: 1.2 }} />
variants
The variants for this component.
const variants = { active: { backgroundColor: "#f00" }, inactive: { backgroundColor: "#fff", transition: { duration: 2 } } } return ( <motion.div variants={variants} animate={isActive ? "active" : "inactive"} /> )
style
The normal React DOM style prop, with added support for motion values and independent transforms.
const x = useMotionValue(30) return <motion.div style={{ x, rotate: 90, originX: 0.5 }} />
onUpdate
Callback triggered every frame any value on the motion component updates. It's provided a single argument with the latest values.
<motion.article animate={{ opacity: 1 }} onUpdate={latest => console.log(latest.opacity)} />
onAnimationStart
Callback triggered when any animation (except layout animations, see onLayoutAnimationStart) starts.
It's provided a single argument, with the target or variant name of the started animation.
<motion.circle animate={{ r: 10 }} onAnimationStart={latest => console.log(latest.r)} />
onAnimationComplete
Callback triggered when any animation (except layout animations, see onLayoutAnimationComplete) completes.
It's provided a single argument, with the target or variant name of the completed animation.
<motion.circle animate={{ r: 10 }} onAnimationComplete={latest => console.log(latest.r)} />
Hover
whileHover
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a hover animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileHover={{ scale: 1.2 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileHover="hovered" />
onHoverStart
Callback function that fires when a pointer starts hovering over the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onHoverStart={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onHoverEnd
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops hovering over the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onHoverEnd={(event) => console.log(event)} />
Tap
whileTap
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a press animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileTap={{ scale: 0.9 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileTap="tapped" />
onTapStart
Callback function that fires when a pointer starts pressing the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTapStart={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onTap
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops pressing the component and the pointer was released inside the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTap={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onTapCancel
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops pressing the component and the pointer was released outside the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTapCancel={(event) => console.log(event)} />
Focus
whileFocus
Animation state, or variant label, to animate to while the focus gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileFocus={{ outline: "dashed #000" }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileFocus="focused" />
Pan
onPan
Callback function that fires when the pan gesture is recognised on this element.
For pan gestures to work correctly with touch input, the element needs touch scrolling to be disabled on either x/y or both axis with the touch-action CSS rule.
function onPan(event, info) { console.log(info.point.x, info.point.y) } <motion.div onPan={onPan} />
Pan and drag events are provided the origin PointerEvent as well as an object info that contains x and y point values for the following:
point: Relative to the device or page.delta: Distance since the last event.offset: Distance from the original event.velocity: Current velocity of the pointer.
onPanStart
Callback function that fires when a pan gesture starts. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div onPanStart={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onPanEnd
Callback function that fires when a pan gesture ends. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div onPanEnd={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
Drag
drag
Default: false
Enable dragging for this element. Set true to drag in both directions. Set "x" or "y" to only drag in a specific direction.
<motion.div drag />
whileDrag
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a drag animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.div drag whileDrag={{ scale: 0.9 }} />
// As variants <motion.div drag whileDrag="dragging" />
dragConstraints
Applies constraints on the draggable area.
Set as an object of optional top, left, right, and bottom values, measured in pixels:
<motion.div drag="x" dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} />
Or as a ref to another element to use its bounding box as the draggable constraints:
const MyComponent = () => { const constraintsRef = useRef(null) return ( <motion.div ref={constraintsRef}> <motion.div drag dragConstraints={constraintsRef} /> </motion.div> ) }
dragSnapToOrigin
Default: false
If true, the draggable element will animate back to its center/origin when released.
<motion.div drag dragSnapToOrigin />
dragElastic
Default: 0.5
The degree of movement allowed outside constraints. 0 = no movement, 1 = full movement.
Set to 0.5 by default. Can also be set as false to disable movement.
By passing an object of top/right/bottom/left, individual values can be set per constraint. Any missing values will be set to 0.
<motion.div drag dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} dragElastic={0.2} />
dragMomentum
Default: true
Apply momentum from the pan gesture to the component when dragging finishes. Set to true by default.
<motion.div drag dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} dragMomentum={false} />
dragTransition
Allows you to change dragging momentum transition. When releasing a draggable element, an animation with type "inertia" starts. The animation is based on your dragging velocity. This property allows you to customize it.
<motion.div drag dragTransition={{ bounceStiffness: 600, bounceDamping: 10 }} />
dragDirectionLock
Default: false
Locks drag direction into the soonest detected direction. For example, if the component is moved more on the x axis than y axis before the drag gesture kicks in, it will only drag on the x axis for the remainder of the gesture.
<motion.div drag dragDirectionLock />
dragPropagation
Default: false
Allows drag gesture propagation to child components.
<motion.div drag="x" dragPropagation />
dragControls
Usually, dragging is initiated by pressing down on a component and moving it. For some use-cases, for instance clicking at an arbitrary point on a video scrubber, we might want to initiate dragging from a different component than the draggable one.
By creating a dragControls using the useDragControls hook, we can pass this into the draggable component's dragControls prop. It exposes a start method that can start dragging from pointer events on other components.
const dragControls = useDragControls() function startDrag(event) { dragControls.start(event, { snapToCursor: true }) } return ( <> <div onPointerDown={startDrag} /> <motion.div drag="x" dragControls={dragControls} /> </> )
Given that by setting dragControls you are taking control of initiating the drag gesture, it is possible to disable the draggable element as the initiator by setting dragListener={false}.
dragListener
Determines whether to trigger the drag gesture from event listeners. If passing dragControls, setting this to false will ensure dragging can only be initiated by the controls, rather than a pointerdown event on the draggable element.
onDrag
Callback function that fires when the drag gesture is recognised on this element.
function onDrag(event, info) { console.log(info.point.x, info.point.y) } <motion.div drag onDrag={onDrag} />
Pan and drag events are provided the origin PointerEvent as well as an object info that contains x and y point values for the following:
point: Relative to the device or page.delta: Distance since the last event.offset: Distance from the original event.velocity: Current velocity of the pointer.
onDragStart
Callback function that fires when a drag gesture starts. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div drag onDragStart={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onDragEnd
Callback function that fires when a drag gesture ends. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div drag onDragEnd={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onDirectionLock
Callback function that fires a drag direction is determined.
<motion.div drag dragDirectionLock onDirectionLock={axis => console.log(axis)} />
Gestures
propagate
Prevent children gestures from propagating to their parents. Currently only supports tap.
<motion.div whileTap={{ scale: 2 }}> // Pressing this button won't fire the above scale animation <motion.button whileTap={{ opacity: 0.8 }} propagate={{ tap: false }} /> </motion.div>
Viewport
Learn more about scroll-triggered animations in React.
whileInView
Target or variants to label to while the element is in view.
// As target <motion.div whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileInView="visible" />
viewport
Options to define how the element is tracked within the viewport.
<motion.section whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} viewport={{ once: true }} />
Available options:
once: Iftrue, once element enters the viewport it won't detect subsequent leave/enter events.root: Therefof an ancestor scrollable element to detect intersections with (instead ofwindow).margin: A margin to add to the viewport to change the detection area. Defaults to"0px". Use multiple values to adjust top/right/bottom/left, e.g."0px -20px 0px 100px".amount: The amount of an element that should enter the viewport to be considered "entered". Either"some","all"or a number between0and1. Defaults to"some".
onViewportEnter
Callback function that fires when an element enters the viewport. Provided the IntersectionObserverEntry with details of the intersection event.
<motion.div onViewportEnter={(entry) => console.log(entry.isIntersecting)} />
onViewportLeave
Callback function that fires when an element enters the viewport. Provided the IntersectionObserverEntry with details of the intersection event.
<motion.div onViewportLeave={(entry) => console.log(entry.intersectionRect)} />
Layout
Learn more about layout animations in React.
layout
Default: false
If true, this component will perform layout animations.
<motion.div layout />
If set to "position" or "size", only its position or size will animate, respectively.
<motion.img layout="position" />
layoutId
If set, this component will animate changes to its layout. Additionally, when a new element enters the DOM and an element already exists with a matching layoutId, it will animate out from the previous element's size/position.
{items.map(item => ( <motion.li layout> {item.name} {item.isSelected && <motion.div layoutId="underline" />} </motion.li> ))}
If the previous component remains in the tree, the two elements will crossfade.
layoutDependency
By default, layout changes are detected every render. To reduce measurements and thus improve performance, you can pass a layoutDependency prop. Measurements will only occur when this value changes.
<motion.nav layout layoutDependency={isOpen} />
layoutScroll
For layout animations to work correctly within scrollable elements, their scroll offset needs measuring. For performance reasons, Framer Motion doesn't measure the scroll offset of every ancestor. Add the layoutScroll prop to elements that should be measured.
<motion.div layoutScroll style={{ overflow: "scroll" }}> <motion.div layout /> </motion.div>
layoutRoot
For layout animations to work correctly within position: fixed elements, we need to account for page scroll. Add layoutRoot to mark an element as position: fixed.
<motion.div layoutRoot style={{ position: "fixed" }}> <motion.div layout /> </motion.div>
onLayoutAnimationStart
A callback to run when a layout animation starts.
onLayoutAnimationComplete
A callback to run when a layout animation completes.
Advanced
inherit
Set to false to prevent a component inheriting or propagating changes in a parent variant.
custom
Custom data to pass through to dynamic variants.
const variants = { visible: (custom) => ({ opacity: 1, transition: { delay: custom * 0.2 } }) } return ( <motion.ul animate="visible"> <motion.li custom={0} variants={variants} /> <motion.li custom={1} variants={variants} /> <motion.li custom={2} variants={variants} /> </motion.ul> )
transformTemplate
By default, transforms are applied in order of translate, scale, rotate and skew.
To change this, transformTemplate can be set as a function that accepts the latest transforms and the generated transform string and returns a new transform string.
// Use the latest transform values <motion.div style={{ x: 0, rotate: 180 }} transformTemplate={ ({ x, rotate }) => `rotate(${rotate}deg) translateX(${x}px)` } />
// Or the generated transform string <motion.div style={{ x: 0, rotate: 180 }} transformTemplate={ (latest, generated) => `translate(-50%, -50%) ${generated}` } />
FAQs
What is the <motion /> component?
<motion /> is a drop-in replacement for HTML and SVG elements that adds animation capabilities. Instead of writing <div>, you write <motion.div>. The element behaves identically but can now accept animation props like animate, whileHover, and transition.
How do I animate an element in React with Motion?
Pass an animate prop to any <motion /> component with the values you want to animate to. For example, <motion.div animate={{ opacity: 1 }} /> will animate opacity from its current value to 1. Motion automatically detects changes and animates between them.
Does <motion /> affect performance?
<motion /> is optimised to animate transform and opacity on the compositor thread wherever possible, avoiding layout and paint. For best performance, prefer animating transform and opacity over properties like width or top.
Can I use <motion /> with custom components?
Yes. Use motion.create() to wrap any component that forwards its ref and accepts a style prop. For example: const MotionButton = motion.create(Button).
Most React animations in Motion are powered by the <motion /> component.
There's a motion component for every HTML and SVG element, for instance motion.div, motion.circle etc. It extends standard React components with animation props that run at up to 120fps - without triggering React re-renders.
Usage
Import motion from Motion:
// React import { motion } from "motion/react" // React Server Components (Next.js etc) import * as motion from "motion/react-client"
You can use a motion component exactly as you would any normal HTML/SVG component:
<motion.div className="box" />
But you also gain access to powerful animation APIs like the animate, layout, whileInView props.
<motion.div className="box" // Animate when this value changes: animate={{ scale: 2 }} // Fade in when the element enters the viewport: whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} // Animate the component when its layout changes: layout // Style now supports indepedent transforms: style={{ x: 100 }} />
Building with AI? The Motion Studio MCP gives your AI editor access to the latest docs and source code of 330+ examples.
Performance
motion components bypass React's render cycle entirely. Animated values update on every frame via the browser's native animation pipeline, so even complex animations with dozens of animated properties won't cause React re-renders or style/layout thrashing.
Using motion values instead of React state to update style will also avoid re-renders.
const x = useMotionValue(0) useEffect(() => { // Won't trigger a re-render! const timeout = setTimeout(() => x.set(100), 1000) return () => clearTimeout(timeout) }, []) return <motion.div style={{ x }} />
Check your MotionScore
Enter a URL to audit your site's animation performance.
Server-side rendering
motion components are fully compatible with server-side rendering, meaning the initial state of the component will be reflected in the server-generated output.
// Server will output `translateX(100px)` <motion.div initial={false} animate={{ x: 100 }} />
Custom components
You can add motion capabilities to any React component with motion.create(). The returned component accepts all standard motion props (animate, whileHover, drag, layout, etc.) alongside the original component's props.
const MotionComponent = motion.create(Component)
Your component must pass a ref to the component you want to animate.
React 18: Use forwardRef to wrap the component and pass ref to the element you want to animate:
const Component = React.forwardRef((props, ref) => { return <div ref={ref} /> })
React 19: React 19 can pass ref via props:
const Component = (props) => { return <div ref={props.ref} /> })
Make sure not to call motion.create() within a React render function! This will make a new component every render, breaking your animations.
It's also possible to pass strings to motion.create, which will create custom DOM elements.
// Will render <custom-element /> into HTML const MotionComponent = motion.create('custom-element')
By default, all motion props (like animate etc) are filtered out of the props forwarded to the provided component. By providing a forwardMotionProps config, the provided component will receive these props.
motion.create(Component, { forwardMotionProps: true })
Stay in the loop
Sign up for the Motion newsletter.
Props
motion components accept the following props.
Animation
Motion provides declarative animation props like animate and exit. Learn more about React animations in Motion.
initial
The initial visual state of the motion component.
This can be set as an animation target:
<motion.section initial={{ opacity: 0, x: 0 }} />
Variants:
<motion.li initial="visible" />
<motion.div initial={["visible", "active"]} />
Or set as false to disable the enter animation and initially render as the values found in animate.
<motion.div initial={false} animate={{ opacity: 0 }} />
animate
A target to animate to on enter, and on update.
Can be set as an animation target:
<motion.div initial={{ boxShadow: "0px 0px #000" }} animate={{ boxShadow: "10px 10px #000" }} />
Or variants:
<motion.li animate="visible" />
<motion.div initial="hidden" animate={["visible", "active"]} />
exit
A target to animate to when a component is removed from the tree. Can be set either as an animation target, or variant.
Owing to React limitations, the component being removed must be a direct child of AnimatePresence to enable this animation.
transition
The default transition for this component to use when an animation prop (animate, whileHover etc) has no transition defined.
<motion.div transition={{ type: "spring" }} animate={{ scale: 1.2 }} />
variants
The variants for this component.
const variants = { active: { backgroundColor: "#f00" }, inactive: { backgroundColor: "#fff", transition: { duration: 2 } } } return ( <motion.div variants={variants} animate={isActive ? "active" : "inactive"} /> )
style
The normal React DOM style prop, with added support for motion values and independent transforms.
const x = useMotionValue(30) return <motion.div style={{ x, rotate: 90, originX: 0.5 }} />
onUpdate
Callback triggered every frame any value on the motion component updates. It's provided a single argument with the latest values.
<motion.article animate={{ opacity: 1 }} onUpdate={latest => console.log(latest.opacity)} />
onAnimationStart
Callback triggered when any animation (except layout animations, see onLayoutAnimationStart) starts.
It's provided a single argument, with the target or variant name of the started animation.
<motion.circle animate={{ r: 10 }} onAnimationStart={latest => console.log(latest.r)} />
onAnimationComplete
Callback triggered when any animation (except layout animations, see onLayoutAnimationComplete) completes.
It's provided a single argument, with the target or variant name of the completed animation.
<motion.circle animate={{ r: 10 }} onAnimationComplete={latest => console.log(latest.r)} />
Hover
whileHover
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a hover animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileHover={{ scale: 1.2 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileHover="hovered" />
onHoverStart
Callback function that fires when a pointer starts hovering over the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onHoverStart={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onHoverEnd
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops hovering over the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onHoverEnd={(event) => console.log(event)} />
Tap
whileTap
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a press animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileTap={{ scale: 0.9 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileTap="tapped" />
onTapStart
Callback function that fires when a pointer starts pressing the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTapStart={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onTap
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops pressing the component and the pointer was released inside the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTap={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onTapCancel
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops pressing the component and the pointer was released outside the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTapCancel={(event) => console.log(event)} />
Focus
whileFocus
Animation state, or variant label, to animate to while the focus gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileFocus={{ outline: "dashed #000" }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileFocus="focused" />
Pan
onPan
Callback function that fires when the pan gesture is recognised on this element.
For pan gestures to work correctly with touch input, the element needs touch scrolling to be disabled on either x/y or both axis with the touch-action CSS rule.
function onPan(event, info) { console.log(info.point.x, info.point.y) } <motion.div onPan={onPan} />
Pan and drag events are provided the origin PointerEvent as well as an object info that contains x and y point values for the following:
point: Relative to the device or page.delta: Distance since the last event.offset: Distance from the original event.velocity: Current velocity of the pointer.
onPanStart
Callback function that fires when a pan gesture starts. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div onPanStart={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onPanEnd
Callback function that fires when a pan gesture ends. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div onPanEnd={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
Drag
drag
Default: false
Enable dragging for this element. Set true to drag in both directions. Set "x" or "y" to only drag in a specific direction.
<motion.div drag />
whileDrag
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a drag animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.div drag whileDrag={{ scale: 0.9 }} />
// As variants <motion.div drag whileDrag="dragging" />
dragConstraints
Applies constraints on the draggable area.
Set as an object of optional top, left, right, and bottom values, measured in pixels:
<motion.div drag="x" dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} />
Or as a ref to another element to use its bounding box as the draggable constraints:
const MyComponent = () => { const constraintsRef = useRef(null) return ( <motion.div ref={constraintsRef}> <motion.div drag dragConstraints={constraintsRef} /> </motion.div> ) }
dragSnapToOrigin
Default: false
If true, the draggable element will animate back to its center/origin when released.
<motion.div drag dragSnapToOrigin />
dragElastic
Default: 0.5
The degree of movement allowed outside constraints. 0 = no movement, 1 = full movement.
Set to 0.5 by default. Can also be set as false to disable movement.
By passing an object of top/right/bottom/left, individual values can be set per constraint. Any missing values will be set to 0.
<motion.div drag dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} dragElastic={0.2} />
dragMomentum
Default: true
Apply momentum from the pan gesture to the component when dragging finishes. Set to true by default.
<motion.div drag dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} dragMomentum={false} />
dragTransition
Allows you to change dragging momentum transition. When releasing a draggable element, an animation with type "inertia" starts. The animation is based on your dragging velocity. This property allows you to customize it.
<motion.div drag dragTransition={{ bounceStiffness: 600, bounceDamping: 10 }} />
dragDirectionLock
Default: false
Locks drag direction into the soonest detected direction. For example, if the component is moved more on the x axis than y axis before the drag gesture kicks in, it will only drag on the x axis for the remainder of the gesture.
<motion.div drag dragDirectionLock />
dragPropagation
Default: false
Allows drag gesture propagation to child components.
<motion.div drag="x" dragPropagation />
dragControls
Usually, dragging is initiated by pressing down on a component and moving it. For some use-cases, for instance clicking at an arbitrary point on a video scrubber, we might want to initiate dragging from a different component than the draggable one.
By creating a dragControls using the useDragControls hook, we can pass this into the draggable component's dragControls prop. It exposes a start method that can start dragging from pointer events on other components.
const dragControls = useDragControls() function startDrag(event) { dragControls.start(event, { snapToCursor: true }) } return ( <> <div onPointerDown={startDrag} /> <motion.div drag="x" dragControls={dragControls} /> </> )
Given that by setting dragControls you are taking control of initiating the drag gesture, it is possible to disable the draggable element as the initiator by setting dragListener={false}.
dragListener
Determines whether to trigger the drag gesture from event listeners. If passing dragControls, setting this to false will ensure dragging can only be initiated by the controls, rather than a pointerdown event on the draggable element.
onDrag
Callback function that fires when the drag gesture is recognised on this element.
function onDrag(event, info) { console.log(info.point.x, info.point.y) } <motion.div drag onDrag={onDrag} />
Pan and drag events are provided the origin PointerEvent as well as an object info that contains x and y point values for the following:
point: Relative to the device or page.delta: Distance since the last event.offset: Distance from the original event.velocity: Current velocity of the pointer.
onDragStart
Callback function that fires when a drag gesture starts. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div drag onDragStart={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onDragEnd
Callback function that fires when a drag gesture ends. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div drag onDragEnd={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onDirectionLock
Callback function that fires a drag direction is determined.
<motion.div drag dragDirectionLock onDirectionLock={axis => console.log(axis)} />
Gestures
propagate
Prevent children gestures from propagating to their parents. Currently only supports tap.
<motion.div whileTap={{ scale: 2 }}> // Pressing this button won't fire the above scale animation <motion.button whileTap={{ opacity: 0.8 }} propagate={{ tap: false }} /> </motion.div>
Viewport
Learn more about scroll-triggered animations in React.
whileInView
Target or variants to label to while the element is in view.
// As target <motion.div whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileInView="visible" />
viewport
Options to define how the element is tracked within the viewport.
<motion.section whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} viewport={{ once: true }} />
Available options:
once: Iftrue, once element enters the viewport it won't detect subsequent leave/enter events.root: Therefof an ancestor scrollable element to detect intersections with (instead ofwindow).margin: A margin to add to the viewport to change the detection area. Defaults to"0px". Use multiple values to adjust top/right/bottom/left, e.g."0px -20px 0px 100px".amount: The amount of an element that should enter the viewport to be considered "entered". Either"some","all"or a number between0and1. Defaults to"some".
onViewportEnter
Callback function that fires when an element enters the viewport. Provided the IntersectionObserverEntry with details of the intersection event.
<motion.div onViewportEnter={(entry) => console.log(entry.isIntersecting)} />
onViewportLeave
Callback function that fires when an element enters the viewport. Provided the IntersectionObserverEntry with details of the intersection event.
<motion.div onViewportLeave={(entry) => console.log(entry.intersectionRect)} />
Layout
Learn more about layout animations in React.
layout
Default: false
If true, this component will perform layout animations.
<motion.div layout />
If set to "position" or "size", only its position or size will animate, respectively.
<motion.img layout="position" />
layoutId
If set, this component will animate changes to its layout. Additionally, when a new element enters the DOM and an element already exists with a matching layoutId, it will animate out from the previous element's size/position.
{items.map(item => ( <motion.li layout> {item.name} {item.isSelected && <motion.div layoutId="underline" />} </motion.li> ))}
If the previous component remains in the tree, the two elements will crossfade.
layoutDependency
By default, layout changes are detected every render. To reduce measurements and thus improve performance, you can pass a layoutDependency prop. Measurements will only occur when this value changes.
<motion.nav layout layoutDependency={isOpen} />
layoutScroll
For layout animations to work correctly within scrollable elements, their scroll offset needs measuring. For performance reasons, Framer Motion doesn't measure the scroll offset of every ancestor. Add the layoutScroll prop to elements that should be measured.
<motion.div layoutScroll style={{ overflow: "scroll" }}> <motion.div layout /> </motion.div>
layoutRoot
For layout animations to work correctly within position: fixed elements, we need to account for page scroll. Add layoutRoot to mark an element as position: fixed.
<motion.div layoutRoot style={{ position: "fixed" }}> <motion.div layout /> </motion.div>
onLayoutAnimationStart
A callback to run when a layout animation starts.
onLayoutAnimationComplete
A callback to run when a layout animation completes.
Advanced
inherit
Set to false to prevent a component inheriting or propagating changes in a parent variant.
custom
Custom data to pass through to dynamic variants.
const variants = { visible: (custom) => ({ opacity: 1, transition: { delay: custom * 0.2 } }) } return ( <motion.ul animate="visible"> <motion.li custom={0} variants={variants} /> <motion.li custom={1} variants={variants} /> <motion.li custom={2} variants={variants} /> </motion.ul> )
transformTemplate
By default, transforms are applied in order of translate, scale, rotate and skew.
To change this, transformTemplate can be set as a function that accepts the latest transforms and the generated transform string and returns a new transform string.
// Use the latest transform values <motion.div style={{ x: 0, rotate: 180 }} transformTemplate={ ({ x, rotate }) => `rotate(${rotate}deg) translateX(${x}px)` } />
// Or the generated transform string <motion.div style={{ x: 0, rotate: 180 }} transformTemplate={ (latest, generated) => `translate(-50%, -50%) ${generated}` } />
FAQs
What is the <motion /> component?
<motion /> is a drop-in replacement for HTML and SVG elements that adds animation capabilities. Instead of writing <div>, you write <motion.div>. The element behaves identically but can now accept animation props like animate, whileHover, and transition.
How do I animate an element in React with Motion?
Pass an animate prop to any <motion /> component with the values you want to animate to. For example, <motion.div animate={{ opacity: 1 }} /> will animate opacity from its current value to 1. Motion automatically detects changes and animates between them.
Does <motion /> affect performance?
<motion /> is optimised to animate transform and opacity on the compositor thread wherever possible, avoiding layout and paint. For best performance, prefer animating transform and opacity over properties like width or top.
Can I use <motion /> with custom components?
Yes. Use motion.create() to wrap any component that forwards its ref and accepts a style prop. For example: const MotionButton = motion.create(Button).
Most React animations in Motion are powered by the <motion /> component.
There's a motion component for every HTML and SVG element, for instance motion.div, motion.circle etc. It extends standard React components with animation props that run at up to 120fps - without triggering React re-renders.
Usage
Import motion from Motion:
// React import { motion } from "motion/react" // React Server Components (Next.js etc) import * as motion from "motion/react-client"
You can use a motion component exactly as you would any normal HTML/SVG component:
<motion.div className="box" />
But you also gain access to powerful animation APIs like the animate, layout, whileInView props.
<motion.div className="box" // Animate when this value changes: animate={{ scale: 2 }} // Fade in when the element enters the viewport: whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} // Animate the component when its layout changes: layout // Style now supports indepedent transforms: style={{ x: 100 }} />
Building with AI? The Motion Studio MCP gives your AI editor access to the latest docs and source code of 330+ examples.
Performance
motion components bypass React's render cycle entirely. Animated values update on every frame via the browser's native animation pipeline, so even complex animations with dozens of animated properties won't cause React re-renders or style/layout thrashing.
Using motion values instead of React state to update style will also avoid re-renders.
const x = useMotionValue(0) useEffect(() => { // Won't trigger a re-render! const timeout = setTimeout(() => x.set(100), 1000) return () => clearTimeout(timeout) }, []) return <motion.div style={{ x }} />
Check your MotionScore
Enter a URL to audit your site's animation performance.
Server-side rendering
motion components are fully compatible with server-side rendering, meaning the initial state of the component will be reflected in the server-generated output.
// Server will output `translateX(100px)` <motion.div initial={false} animate={{ x: 100 }} />
Custom components
You can add motion capabilities to any React component with motion.create(). The returned component accepts all standard motion props (animate, whileHover, drag, layout, etc.) alongside the original component's props.
const MotionComponent = motion.create(Component)
Your component must pass a ref to the component you want to animate.
React 18: Use forwardRef to wrap the component and pass ref to the element you want to animate:
const Component = React.forwardRef((props, ref) => { return <div ref={ref} /> })
React 19: React 19 can pass ref via props:
const Component = (props) => { return <div ref={props.ref} /> })
Make sure not to call motion.create() within a React render function! This will make a new component every render, breaking your animations.
It's also possible to pass strings to motion.create, which will create custom DOM elements.
// Will render <custom-element /> into HTML const MotionComponent = motion.create('custom-element')
By default, all motion props (like animate etc) are filtered out of the props forwarded to the provided component. By providing a forwardMotionProps config, the provided component will receive these props.
motion.create(Component, { forwardMotionProps: true })
Stay in the loop
Sign up for the Motion newsletter.
Props
motion components accept the following props.
Animation
Motion provides declarative animation props like animate and exit. Learn more about React animations in Motion.
initial
The initial visual state of the motion component.
This can be set as an animation target:
<motion.section initial={{ opacity: 0, x: 0 }} />
Variants:
<motion.li initial="visible" />
<motion.div initial={["visible", "active"]} />
Or set as false to disable the enter animation and initially render as the values found in animate.
<motion.div initial={false} animate={{ opacity: 0 }} />
animate
A target to animate to on enter, and on update.
Can be set as an animation target:
<motion.div initial={{ boxShadow: "0px 0px #000" }} animate={{ boxShadow: "10px 10px #000" }} />
Or variants:
<motion.li animate="visible" />
<motion.div initial="hidden" animate={["visible", "active"]} />
exit
A target to animate to when a component is removed from the tree. Can be set either as an animation target, or variant.
Owing to React limitations, the component being removed must be a direct child of AnimatePresence to enable this animation.
transition
The default transition for this component to use when an animation prop (animate, whileHover etc) has no transition defined.
<motion.div transition={{ type: "spring" }} animate={{ scale: 1.2 }} />
variants
The variants for this component.
const variants = { active: { backgroundColor: "#f00" }, inactive: { backgroundColor: "#fff", transition: { duration: 2 } } } return ( <motion.div variants={variants} animate={isActive ? "active" : "inactive"} /> )
style
The normal React DOM style prop, with added support for motion values and independent transforms.
const x = useMotionValue(30) return <motion.div style={{ x, rotate: 90, originX: 0.5 }} />
onUpdate
Callback triggered every frame any value on the motion component updates. It's provided a single argument with the latest values.
<motion.article animate={{ opacity: 1 }} onUpdate={latest => console.log(latest.opacity)} />
onAnimationStart
Callback triggered when any animation (except layout animations, see onLayoutAnimationStart) starts.
It's provided a single argument, with the target or variant name of the started animation.
<motion.circle animate={{ r: 10 }} onAnimationStart={latest => console.log(latest.r)} />
onAnimationComplete
Callback triggered when any animation (except layout animations, see onLayoutAnimationComplete) completes.
It's provided a single argument, with the target or variant name of the completed animation.
<motion.circle animate={{ r: 10 }} onAnimationComplete={latest => console.log(latest.r)} />
Hover
whileHover
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a hover animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileHover={{ scale: 1.2 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileHover="hovered" />
onHoverStart
Callback function that fires when a pointer starts hovering over the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onHoverStart={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onHoverEnd
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops hovering over the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onHoverEnd={(event) => console.log(event)} />
Tap
whileTap
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a press animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileTap={{ scale: 0.9 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileTap="tapped" />
onTapStart
Callback function that fires when a pointer starts pressing the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTapStart={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onTap
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops pressing the component and the pointer was released inside the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTap={(event) => console.log(event)} />
onTapCancel
Callback function that fires when a pointer stops pressing the component and the pointer was released outside the component. Provided the triggering PointerEvent.
<motion.div onTapCancel={(event) => console.log(event)} />
Focus
whileFocus
Animation state, or variant label, to animate to while the focus gesture is active.
// As target <motion.button whileFocus={{ outline: "dashed #000" }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileFocus="focused" />
Pan
onPan
Callback function that fires when the pan gesture is recognised on this element.
For pan gestures to work correctly with touch input, the element needs touch scrolling to be disabled on either x/y or both axis with the touch-action CSS rule.
function onPan(event, info) { console.log(info.point.x, info.point.y) } <motion.div onPan={onPan} />
Pan and drag events are provided the origin PointerEvent as well as an object info that contains x and y point values for the following:
point: Relative to the device or page.delta: Distance since the last event.offset: Distance from the original event.velocity: Current velocity of the pointer.
onPanStart
Callback function that fires when a pan gesture starts. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div onPanStart={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onPanEnd
Callback function that fires when a pan gesture ends. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div onPanEnd={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
Drag
drag
Default: false
Enable dragging for this element. Set true to drag in both directions. Set "x" or "y" to only drag in a specific direction.
<motion.div drag />
whileDrag
Animation state, or variant label, to perform a drag animation to while the hover gesture is active.
// As target <motion.div drag whileDrag={{ scale: 0.9 }} />
// As variants <motion.div drag whileDrag="dragging" />
dragConstraints
Applies constraints on the draggable area.
Set as an object of optional top, left, right, and bottom values, measured in pixels:
<motion.div drag="x" dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} />
Or as a ref to another element to use its bounding box as the draggable constraints:
const MyComponent = () => { const constraintsRef = useRef(null) return ( <motion.div ref={constraintsRef}> <motion.div drag dragConstraints={constraintsRef} /> </motion.div> ) }
dragSnapToOrigin
Default: false
If true, the draggable element will animate back to its center/origin when released.
<motion.div drag dragSnapToOrigin />
dragElastic
Default: 0.5
The degree of movement allowed outside constraints. 0 = no movement, 1 = full movement.
Set to 0.5 by default. Can also be set as false to disable movement.
By passing an object of top/right/bottom/left, individual values can be set per constraint. Any missing values will be set to 0.
<motion.div drag dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} dragElastic={0.2} />
dragMomentum
Default: true
Apply momentum from the pan gesture to the component when dragging finishes. Set to true by default.
<motion.div drag dragConstraints={{ left: 0, right: 300 }} dragMomentum={false} />
dragTransition
Allows you to change dragging momentum transition. When releasing a draggable element, an animation with type "inertia" starts. The animation is based on your dragging velocity. This property allows you to customize it.
<motion.div drag dragTransition={{ bounceStiffness: 600, bounceDamping: 10 }} />
dragDirectionLock
Default: false
Locks drag direction into the soonest detected direction. For example, if the component is moved more on the x axis than y axis before the drag gesture kicks in, it will only drag on the x axis for the remainder of the gesture.
<motion.div drag dragDirectionLock />
dragPropagation
Default: false
Allows drag gesture propagation to child components.
<motion.div drag="x" dragPropagation />
dragControls
Usually, dragging is initiated by pressing down on a component and moving it. For some use-cases, for instance clicking at an arbitrary point on a video scrubber, we might want to initiate dragging from a different component than the draggable one.
By creating a dragControls using the useDragControls hook, we can pass this into the draggable component's dragControls prop. It exposes a start method that can start dragging from pointer events on other components.
const dragControls = useDragControls() function startDrag(event) { dragControls.start(event, { snapToCursor: true }) } return ( <> <div onPointerDown={startDrag} /> <motion.div drag="x" dragControls={dragControls} /> </> )
Given that by setting dragControls you are taking control of initiating the drag gesture, it is possible to disable the draggable element as the initiator by setting dragListener={false}.
dragListener
Determines whether to trigger the drag gesture from event listeners. If passing dragControls, setting this to false will ensure dragging can only be initiated by the controls, rather than a pointerdown event on the draggable element.
onDrag
Callback function that fires when the drag gesture is recognised on this element.
function onDrag(event, info) { console.log(info.point.x, info.point.y) } <motion.div drag onDrag={onDrag} />
Pan and drag events are provided the origin PointerEvent as well as an object info that contains x and y point values for the following:
point: Relative to the device or page.delta: Distance since the last event.offset: Distance from the original event.velocity: Current velocity of the pointer.
onDragStart
Callback function that fires when a drag gesture starts. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div drag onDragStart={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onDragEnd
Callback function that fires when a drag gesture ends. Provided the triggering PointerEvent and info.
<motion.div drag onDragEnd={(event, info) => console.log(info.delta.x)} />
onDirectionLock
Callback function that fires a drag direction is determined.
<motion.div drag dragDirectionLock onDirectionLock={axis => console.log(axis)} />
Gestures
propagate
Prevent children gestures from propagating to their parents. Currently only supports tap.
<motion.div whileTap={{ scale: 2 }}> // Pressing this button won't fire the above scale animation <motion.button whileTap={{ opacity: 0.8 }} propagate={{ tap: false }} /> </motion.div>
Viewport
Learn more about scroll-triggered animations in React.
whileInView
Target or variants to label to while the element is in view.
// As target <motion.div whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} />
// As variants <motion.div whileInView="visible" />
viewport
Options to define how the element is tracked within the viewport.
<motion.section whileInView={{ opacity: 1 }} viewport={{ once: true }} />
Available options:
once: Iftrue, once element enters the viewport it won't detect subsequent leave/enter events.root: Therefof an ancestor scrollable element to detect intersections with (instead ofwindow).margin: A margin to add to the viewport to change the detection area. Defaults to"0px". Use multiple values to adjust top/right/bottom/left, e.g."0px -20px 0px 100px".amount: The amount of an element that should enter the viewport to be considered "entered". Either"some","all"or a number between0and1. Defaults to"some".
onViewportEnter
Callback function that fires when an element enters the viewport. Provided the IntersectionObserverEntry with details of the intersection event.
<motion.div onViewportEnter={(entry) => console.log(entry.isIntersecting)} />
onViewportLeave
Callback function that fires when an element enters the viewport. Provided the IntersectionObserverEntry with details of the intersection event.
<motion.div onViewportLeave={(entry) => console.log(entry.intersectionRect)} />
Layout
Learn more about layout animations in React.
layout
Default: false
If true, this component will perform layout animations.
<motion.div layout />
If set to "position" or "size", only its position or size will animate, respectively.
<motion.img layout="position" />
layoutId
If set, this component will animate changes to its layout. Additionally, when a new element enters the DOM and an element already exists with a matching layoutId, it will animate out from the previous element's size/position.
{items.map(item => ( <motion.li layout> {item.name} {item.isSelected && <motion.div layoutId="underline" />} </motion.li> ))}
If the previous component remains in the tree, the two elements will crossfade.
layoutDependency
By default, layout changes are detected every render. To reduce measurements and thus improve performance, you can pass a layoutDependency prop. Measurements will only occur when this value changes.
<motion.nav layout layoutDependency={isOpen} />
layoutScroll
For layout animations to work correctly within scrollable elements, their scroll offset needs measuring. For performance reasons, Framer Motion doesn't measure the scroll offset of every ancestor. Add the layoutScroll prop to elements that should be measured.
<motion.div layoutScroll style={{ overflow: "scroll" }}> <motion.div layout /> </motion.div>
layoutRoot
For layout animations to work correctly within position: fixed elements, we need to account for page scroll. Add layoutRoot to mark an element as position: fixed.
<motion.div layoutRoot style={{ position: "fixed" }}> <motion.div layout /> </motion.div>
onLayoutAnimationStart
A callback to run when a layout animation starts.
onLayoutAnimationComplete
A callback to run when a layout animation completes.
Advanced
inherit
Set to false to prevent a component inheriting or propagating changes in a parent variant.
custom
Custom data to pass through to dynamic variants.
const variants = { visible: (custom) => ({ opacity: 1, transition: { delay: custom * 0.2 } }) } return ( <motion.ul animate="visible"> <motion.li custom={0} variants={variants} /> <motion.li custom={1} variants={variants} /> <motion.li custom={2} variants={variants} /> </motion.ul> )
transformTemplate
By default, transforms are applied in order of translate, scale, rotate and skew.
To change this, transformTemplate can be set as a function that accepts the latest transforms and the generated transform string and returns a new transform string.
// Use the latest transform values <motion.div style={{ x: 0, rotate: 180 }} transformTemplate={ ({ x, rotate }) => `rotate(${rotate}deg) translateX(${x}px)` } />
// Or the generated transform string <motion.div style={{ x: 0, rotate: 180 }} transformTemplate={ (latest, generated) => `translate(-50%, -50%) ${generated}` } />
FAQs
What is the <motion /> component?
<motion /> is a drop-in replacement for HTML and SVG elements that adds animation capabilities. Instead of writing <div>, you write <motion.div>. The element behaves identically but can now accept animation props like animate, whileHover, and transition.
How do I animate an element in React with Motion?
Pass an animate prop to any <motion /> component with the values you want to animate to. For example, <motion.div animate={{ opacity: 1 }} /> will animate opacity from its current value to 1. Motion automatically detects changes and animates between them.
Does <motion /> affect performance?
<motion /> is optimised to animate transform and opacity on the compositor thread wherever possible, avoiding layout and paint. For best performance, prefer animating transform and opacity over properties like width or top.
Can I use <motion /> with custom components?
Yes. Use motion.create() to wrap any component that forwards its ref and accepts a style prop. For example: const MotionButton = motion.create(Button).